Diez de Bonilla Kuri y Asociados
07/10/2025

New STPS Provisions on the Right to Rest for Workers in Standing Positions
The Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare (STPS) has issued Provisions on risk factors to ensure the right to rest during the workday for workers performing standing activities (bipedestation).
Objective: Establish minimum requirements for employers to provide a sufficient number and type of appropriate seats/chairs with backrests.
Scope: Mandatory for all workplaces in national territory within the services, commerce, and analogous sectors; and in industrial establishments when the nature of the work allows it.
Effective date: July 17, 2025.
What do they establish?
- They define types of standing work (static, dynamic, and prolonged when exceeding 3 continuous hours) and the risk factors to be considered (time, posture, mobility, rest breaks, surface, and job position).
- Employers must perform a risk analysis/assessment regarding standing work and integrate it into the occupational safety and health program/assessment (NOM-030-STPS-2009), considering the following diagram:
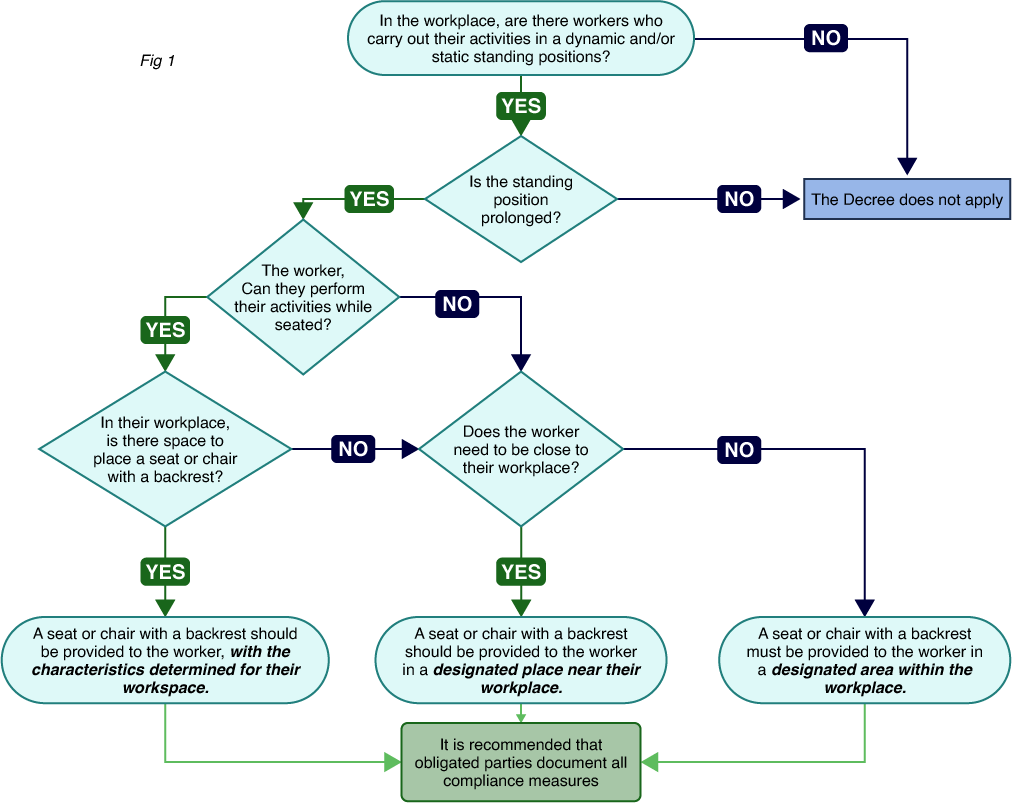
- They must record in the Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes the detected risks and preventive measures (record including data of the workplace, area, tasks, type of standing work, time, age/gender/pregnancy, name of evaluator, etc.).
- They establish a scoring procedure to determine the individual risk level.
- Employers must provide, according to the results, appropriate seats/chairs with backrests (suggested types: high stool, high chair with medium backrest, adjustable ergonomic chair, footrest) with ergonomic features (lumbar support, adjustable height/depth/tilt, stability, ease of movement, armrests/footrests when applicable).
- Additional preventive measures must be implemented (design/adaptation of workstations, alternation of sitting/standing tasks, ergonomic footwear, anti-fatigue surfaces, active break programs).
- Employers must inform and train workers on risks and on the use/maintenance of the seats; mark areas where the seats are located if they are outside the work area.
- Workers showing signs or symptoms associated with standing work must be referred for medical attention.
- They also establish obligations for workers (provide information, participate in training, use and care for the seats, report anomalies, undergo medical exams).
Practical and immediate obligations for companies
- Promptly conduct the required diagnosis/record as established by the regulation (to be included in the occupational safety and health program).
- Apply the scoring procedure to identify individual risk levels per worker.
- Acquire/provide seats/chairs with the required ergonomic features according to the evaluation.
- Adapt workstations and consider anti-fatigue flooring and ergonomic footwear when applicable.
- Establish and document active breaks and task alternation when necessary.
- Update the Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes and keep records with the required information.
- Train staff on risks, use, and maintenance of the seats; mark areas when applicable.
- Establish a mechanism for detecting and referring workers with symptoms to medical attention.
- Review contracts and internal policies to incorporate these obligations and ensure compliance (the STPS will monitor enforcement).
Risks for non-compliance
Inspection and sanctions by the STPS pursuant to the Federal Labor Law and applicable regulations; possible labor and social security liabilities.
Summary recommendation (short checklist)
1.- Schedule diagnosis and assessment of standing work (including scoring).
2.- Update safety and health program/records and Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes.
3.- Purchase/install ergonomic chairs according to results.
4.- Implement active breaks, task alternation, and technical measures.
5.- Train and communicate with workers.
6.- Establish medical referral and follow-up for cases.

New STPS Provisions on the Right to Rest for Workers in Standing Positions
Diez de Bonilla Kuri y Asociados
07/10/2025
The Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare (STPS) has issued Provisions on risk factors to ensure the right to rest during the workday for workers performing standing activities (bipedestation).
Objective: Establish minimum requirements for employers to provide a sufficient number and type of appropriate seats/chairs with backrests.
Scope: Mandatory for all workplaces in national territory within the services, commerce, and analogous sectors; and in industrial establishments when the nature of the work allows it.
Effective date: July 17, 2025.
What do they establish?
- They define types of standing work (static, dynamic, and prolonged when exceeding 3 continuous hours) and the risk factors to be considered (time, posture, mobility, rest breaks, surface, and job position).
- Employers must perform a risk analysis/assessment regarding standing work and integrate it into the occupational safety and health program/assessment (NOM-030-STPS-2009), considering the following diagram:

- They must record in the Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes the detected risks and preventive measures (record including data of the workplace, area, tasks, type of standing work, time, age/gender/pregnancy, name of evaluator, etc.).
- They establish a scoring procedure to determine the individual risk level.
- Employers must provide, according to the results, appropriate seats/chairs with backrests (suggested types: high stool, high chair with medium backrest, adjustable ergonomic chair, footrest) with ergonomic features (lumbar support, adjustable height/depth/tilt, stability, ease of movement, armrests/footrests when applicable).
- Additional preventive measures must be implemented (design/adaptation of workstations, alternation of sitting/standing tasks, ergonomic footwear, anti-fatigue surfaces, active break programs).
- Employers must inform and train workers on risks and on the use/maintenance of the seats; mark areas where the seats are located if they are outside the work area.
- Workers showing signs or symptoms associated with standing work must be referred for medical attention.
- They also establish obligations for workers (provide information, participate in training, use and care for the seats, report anomalies, undergo medical exams).
Practical and immediate obligations for companies
- Promptly conduct the required diagnosis/record as established by the regulation (to be included in the occupational safety and health program).
- Apply the scoring procedure to identify individual risk levels per worker.
- Acquire/provide seats/chairs with the required ergonomic features according to the evaluation.
- Adapt workstations and consider anti-fatigue flooring and ergonomic footwear when applicable.
- Establish and document active breaks and task alternation when necessary.
- Update the Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes and keep records with the required information.
- Train staff on risks, use, and maintenance of the seats; mark areas when applicable.
- Establish a mechanism for detecting and referring workers with symptoms to medical attention.
- Review contracts and internal policies to incorporate these obligations and ensure compliance (the STPS will monitor enforcement).
Risks for non-compliance
Inspection and sanctions by the STPS pursuant to the Federal Labor Law and applicable regulations; possible labor and social security liabilities.
Summary recommendation (short checklist)
1.- Schedule diagnosis and assessment of standing work (including scoring).
2.- Update safety and health program/records and Safety and Hygiene Commission minutes.
3.- Purchase/install ergonomic chairs according to results.
4.- Implement active breaks, task alternation, and technical measures.
5.- Train and communicate with workers.
6.- Establish medical referral and follow-up for cases.

